Regulation Change

The next few years may bring far-reaching regulatory changes. Meanwhile, new technologies in areas such as renewables and self-driving vehicles plus changes to environmental laws will affect business and society profoundly. Read Athena’s partial forecast of what’s likely to emerge.
What is changing?
- Putting hands-free driving on highways within five years will require laws and regulations to keep up with technological advances.
- U.S. generation capacity is projected to jump more than 50 percent by 2040, even in the absence of new environmental regulations requiring renewables.
- Objective-based regulation is considered to be the most suitable form of regulation to manage the environmental risks associated with oil and gas activities.
- There are some areas of the relationship between the UK and EU relevant to pharmacology, such as in drug development and drug regulation, that will prove particularly challenging.
- TTIP threatens the EU's ability to limit exposure to toxic chemicals by undermining its more precautionary approach to regulation.
- The UK will have to negotiate new terms for its fisheries with the EU and with other countries in whose waters they are currently fishing.
- Germany and Italy are projected to drive the bioplastics & biopolymers market market in the region owing to the stringent environmental regulations.
- The UK will lose access to the mechanisms of consultation and information exchange that are established under the EU Common Position and Dual-use Regulation.
- The UK used existing national laws and regulations to implement the EU's ICT Directive so there is no reason why the freedoms UK companies have gained to export military equipment to EU member states will be taken away post-Brexit.
- The EU will make sure that the efficiency of UK banks is eroded over time with taxes and regulations.
- UK companies wishing to export to the EU will need to comply with both UK domestic legislation and EU rules.
- The UK will almost be expected to continue to comply with EU environmental law.
- Brexit does represent an opportunity not to blindly harmonize all EU laws and regulations.
- The flood of new regulation from Europe will be halted in the UK.
- EU companies will now demand that their cloud vendors move data out of the UK and into EU data centers to comply with the EU GDPR.
- U.S. cloud providers are building out data centers in the European Union as well as the U.K. Now that the U.K. has decided to leave the EU there will be new laws and regulations in place for cloud providers.
- Government regulations promoting bio-based product usage especially in Europe and North America is expected to drive market growth over the foreseeable future.
- Some environmentalists worry that Britain's departure from the EU will result in the watering down of environmental and climate policy.
- All new type-approved gasoline-powered vehicles in the EU will have to reduce their particulate matter levels to a tenth of the previous amount under the upcoming Euro 6c regulation.
- New landfills will have to install a gas collection control system if non-methane organic compounds exceed 34 metric tons per year.
- From 2018, large ships (over 5 000 gross tonnes) using EU ports will have to report their verified annual CO 2 emissions and other relevant information.
- The convergence of safety, security and privacy concerns will have a huge impact on the future of drones.
- Over-regulation will have a dramatically negative effect on the potential of the drone marketplace.
- Capturing emissions could keep carbon-heavy assets from being retired early ("stranded") in the face of increasingly stringent emissions limits or mounting fines.
- OEMs will have to pay at least €95 for every gram of CO2 above the set limit (95g) multiplied by total cars sold in 2020.
- The stringent environmental regulations in North America and Europe will drive the demand for water-borne formulations in architectural application due to presence of non-hazardous chemicals.
- Global chemical salt demand will be offset to a certain extent by a European Union
- regulation set to take effect in December 2017 that will ban mercury-based chlorine production.
- COP21 will necessitate political change more than it will require dramatic changes to prescriptive environmental law.
- The replacement of a coal-fired power plant by a wind farm will result in much less need for environmental law.
- TTIP threatens the EU's ability to limit exposure to toxic chemicals by undermining its more precautionary approach to regulation.
- Bitcoin and other digital currencies would be included in the EU's anti-money laundering regulation that will be enacted at the end of 2016.
- Objective-based regulation is considered to be the most suitable form of regulation to manage the environmental risks associated with oil and gas activities.
- Regulations encouraging higher energy efficiency and consumer demand for better sound insulation will maintain plastic foam as a strong competitor to fiberglass insulation.
Implications
- Machine-readable regulation would allow more automation and could significantly reduce the cost of change.
- The United States could develop a federal standard for e-waste recycling.
- The EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) will likely further limit digital innovation in EU member nations.
- The UK could significantly improve its growth through Brexit.
- More regulations aimed at bitcoin and digital currencies could be forthcoming in Japan.
- Tech bosses fret that Britain and the EU will end up with different policies towards their most important resource: data.
- Waste-based regulations will drive down the use of foam in disposable packaging.
- EU companies will now demand that their cloud vendors move data out of the UK and into EU data centers to comply with the EU GDPR.
Sentiment (How is the world feeling about regulation changes)
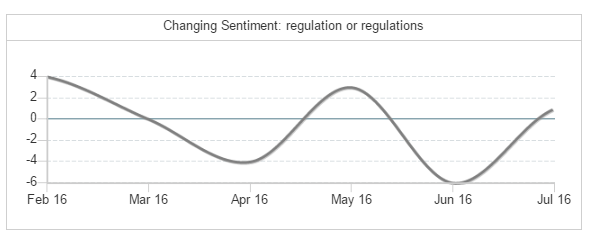
Forecast:
Insight: