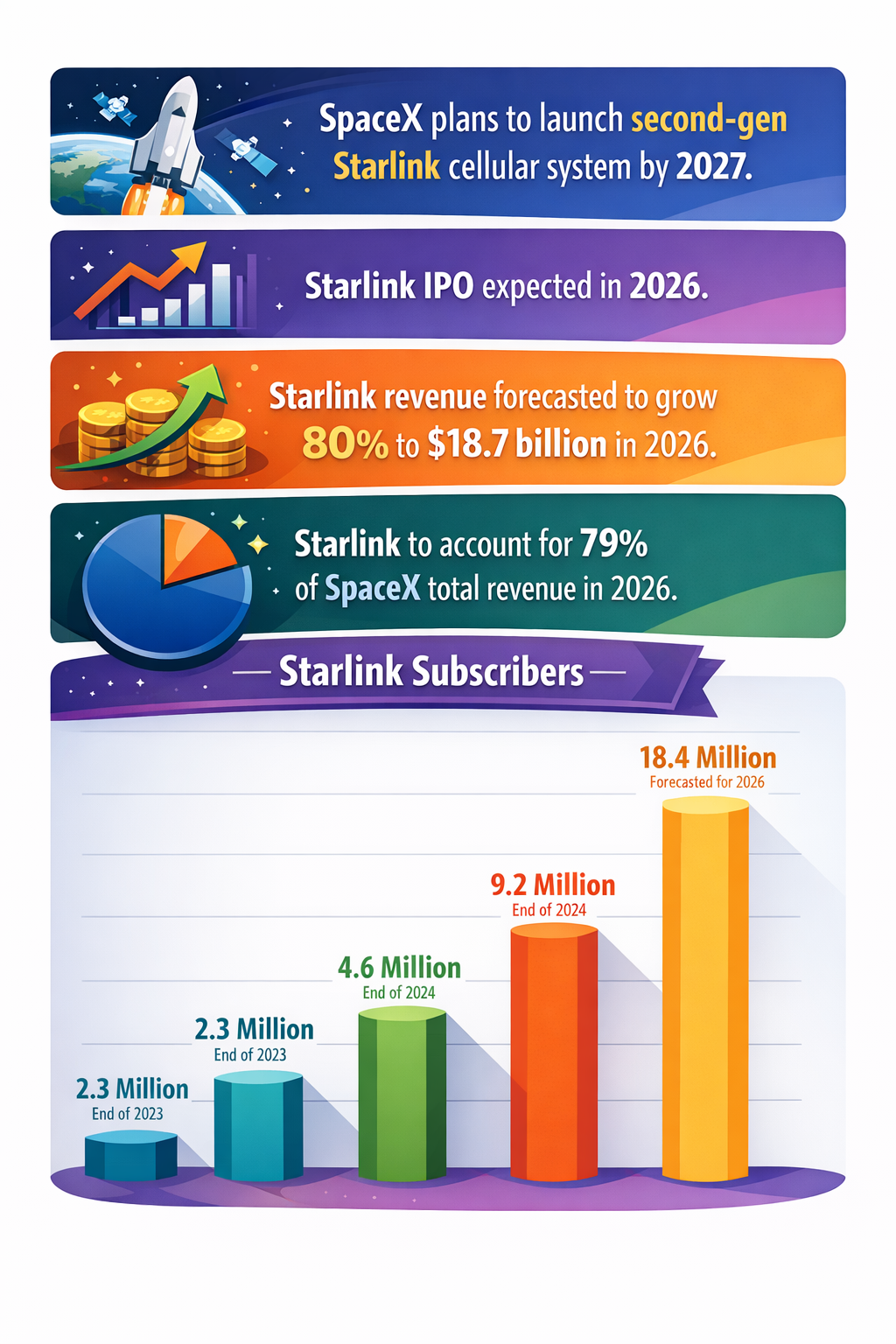
The Emerging Disruption of Satellite-Enabled Direct-to-Device Connectivity
Satellite internet has historically played a supporting role in global communications, primarily catering to remote locations or specialized sectors such as maritime and aviation. Recent innovation in satellite-to-device (D2D) connectivity, however, signals a potential paradigm shift that could redefine global digital infrastructure. This weak signal—where satellites directly enable smartphones and IoT devices to stay connected without traditional cellular networks—could become a major trend disrupting telecoms, defense, logistics, and smart city development in the next 5 to 20 years.
What's Changing?
Major players in space technology and telecommunications are advancing direct-to-device satellite connectivity at a rapid pace. Starlink, SpaceX's low earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellation, has begun enabling text and data messaging on devices even where conventional cellular networks are absent. Early adopters of this service are already leveraging it for uninterrupted communication in the most remote areas, an innovation described in reports involving NTT Docomo’s collaboration with Starlink (itbusinesstoday.com).
This nascent capability is expected to scale swiftly. Starlink’s subscriber base has doubled repeatedly—from 2.3 million users at the end of 2023 to a projected 18.4 million by the end of 2026—indicating robust market demand (aol.com). Moreover, SpaceX aims to launch a second-generation Starlink cellular system by 2027 that could deliver 5G cellular connectivity directly from space, further blending satellite and terrestrial network services (stocktwits.com).
This transformation is not limited to SpaceX. Multiple actors including Amazon are investing heavily in LEO satellite infrastructure and integrating satellite data centers with fiber optics to bolster global coverage and capacity (yahoo.com). China plans to launch up to 200,000 small satellites within seven years, signaling a significant escalation in competitive capacity that may profoundly alter the geopolitical security environment in Northeast Asia (asiae.co.kr).
Technological and market trends that support this shift include:
- Rapid expansion of edge data centers enables localized processing for IoT and AI, integrating seamlessly with satellite data streams (openpr.com).
- Acceleration of 5G technology and in-house chip development, as seen with Apple preparing their own 5G/Wi-Fi chips, allows better compatibility with satellite networks (vietnamnet.vn).
- Telecom operators in emerging markets, such as Airtel in Nigeria, are leveraging D2D satellite partnerships to bring connectivity to underserved rural populations, enabling expansion of digital and fintech services (businesspost.ng).
These developments create an ecosystem where universal connectivity could become a viable reality, breaking geographic and infrastructure limitations. Satellite D2D may evolve from a niche technology to a foundational component of global IoT, smart cities, emergency services, and defense communications.
Why is this Important?
The emergence of satellite D2D connectivity could reshape multiple sectors by fundamentally changing access, reliability, and control of digital communications.
Telecommunications and Internet Access: The reliance on terrestrial cellular networks currently leaves gaps in rural, maritime, and aerial zones. Satellite D2D extends connectivity into these dead zones, democratizing internet access and enabling new services in previously inaccessible areas.
Smart Cities and Urban Analytics: Billions of Internet of Things (IoT) devices generate immense data needed for efficient urban planning and operations. Satellites could serve as a resilient communication backbone that handles wide-area sensor data traffic independently of vulnerable ground-based infrastructure (globenewswire.com).
Healthcare and Emergency Services: South Korea and China are investing in 6G healthcare innovations coupled with satellite networks, potentially enabling faster emergency response and seamless medical data transmission even in disaster-stricken or remote regions (globenewswire.com).
Defense and Security: Situational awareness and command operations increasingly depend on resilient, secure communications. Satellite D2D connectivity is reported to degrade adversary command systems while supporting dispersed and mobile forces, highlighting its strategic significance (criticalthreats.org).
Industry and Logistics: The seamless connection of IoT sensors across supply chains and industrial zones could enhance automation and data-driven decision-making, impacting manufacturing and distribution networks.
Implications
Satellite-to-device connectivity could catalyze major industry transformations over coming decades, but also introduces complex challenges for stakeholders across government, business, and civil society.
For Telecom Operators: Traditional mobile network operators may face disruption as satellite constellations erode their exclusive control over last-mile connectivity. Partnerships or vertical integration into satellite services could become critical survival strategies.
For Regulators and Governments: Spectrum allocation, space traffic management, security, and privacy frameworks require urgent modernization to accommodate rapid LEO constellation growth and direct-to-device services. Geopolitical competition in satellite deployments—particularly in contested regions like Northeast Asia—may escalate tensions and demand new diplomatic mechanisms.
For Business and Industry: Enterprises should evaluate satellite D2D as a compelling option to enhance network resilience, disaster recovery capabilities, and IoT deployments. Early pilots could focus on remote operations, supply chain digitization, and edge computing integration.
For Society and Consumers: Universal connectivity could address digital divides and enhance access to education, health, and financial services. However, disparities in device compatibility, cost, and digital literacy may perpetuate inequalities that require proactive mitigation.
Technical and Environmental Considerations: The rapid launch of thousands or potentially hundreds of thousands of satellites raises concerns around orbital debris, sustainability, and long-term space environment stability. Collaborative governance and innovative technologies such as on-orbit servicing may be needed to manage this ecosystem responsibly.
Questions
- How can telecom operators and satellite providers collaborate to create integrated hybrid networks that maximize coverage and service quality?
- What regulatory frameworks need updating to govern spectrum, security, and debris management for large LEO constellations?
- How might satellite D2D reshape strategies around smart city infrastructure, emergency response, and rural broadband investment?
- What opportunities does satellite D2D connectivity create for accelerated IoT and AI adoption across industries?
- How can governments and businesses mitigate environmental and security risks associated with rapid satellite constellation deployment?
Keywords
Satellite Connectivity; Direct-to-Device Communication; Low Earth Orbit Satellites; 5G; Internet of Things; Edge Computing; Smart Cities; Telecommunications; Orbital Debris; Digital Divide
Bibliography
- NTT Docomo readies satellite direct-to-device service to bring connectivity everywhere. IT Business Today. https://itbusinesstoday.com/industrial-tech/aerospace/ntt-docomo-readies-satellite-direct-to-device-service-to-bring-connectivity-everywhere/
- Starlink subscribers doubled again in 2025, could double again in 2026. AOL Finance. https://www.aol.com/finance/why-2026-spacex-ipo-actually-102500527.html
- SpaceX eyes 2027 launch for Starlink Gen 2 cellular network. Stocktwits. https://stocktwits.com/news-articles/markets/equity/space-x-eyes-2027-launch-for-starlink-gen-2-cellular-network/cmUzVzfR4Q9
- Amazon announces $200B 2026 capex, expands satellite and fiber infrastructure. Yahoo Finance. https://ca.finance.yahoo.com/news/amazon-announces-200b-2026-capex-155235079.html
- China could launch 200,000 satellites to surpass Starlink. Asia Economy. https://cm.asiae.co.kr/en/article/2026020616294372110
- Smart Cities Market projected to generate US$944.68 billion by 2032. Globe Newswire. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2026/02/09/3234330/0/en/Smart-Cities-Market-Projected-to-Generate-US-944-68-Billion-by-2032.html
- Impact of satellite connectivity on Russian command operations. Critical Threats. https://www.criticalthreats.org/analysis/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-february-8-2026
- 3D Printing and 6G healthcare innovations fueled by satellite tech. Globe Newswire. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2026/02/10/3235613/0/en/Global-Markets-Witness-Explosive-Growth-3D-Printing-for-Construction-Leads-with-Highest-CAGR-of-95-5-by-2030.html
- Edge computing market to reach USD 156.2 billion by 2030 at 16.3% CAGR. OpenPR Newswire. https://www.openpr.com/news/4384569/edge-computing-market-to-reach-usd-156-2-billion-by-2030-at-16-3